Introduction Of Silicone Material
Silicone is a versatile material that has become increasingly popular in a wide range of industries. From construction and engineering to personal care and beauty products, silicone is used in a variety of applications due to its unique properties. But what exactly is silicone? In simple terms, silicone is a synthetic polymer that is made up of silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen atoms. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the properties of silicone, its uses, how it’s made, and safety and environmental considerations.
Brief history of silicone
Silicone was first discovered in the early 19th century by a Swedish chemist named Jöns Jacob Berzelius. Berzelius was studying the chemical composition of various minerals when he isolated a new element, silicon, which he named after the Latin word for flint, “silex”. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that silicone as we know it today was developed.
In 1930, the first silicone polymer was created by a chemist named Eugene Rochow at the General Electric Company. Rochow was trying to find a way to produce a synthetic substitute for rubber, which was in short supply at the time. He discovered that by reacting silicon with methyl chloride, he could create a new material with unique properties, including high heat resistance and low chemical reactivity.
During World War II, silicone gained further attention as a potential replacement for rubber in military applications. Silicone was used to make gaskets, seals, and other components for military equipment, and its superior properties quickly made it a popular alternative to traditional rubber.
In the decades that followed, silicone continued to gain popularity in a wide range of industries, from aerospace and automotive to construction and medical. Today, silicone is used in everything from sealants and adhesives to cooking utensils and personal care products.
Properties of Silicone
Chemical structure of silicone
Silicone is a synthetic polymer that is made up of repeating units of siloxane, which is a chain of alternating silicon and oxygen atoms. The chemical formula for silicone is generally written as R2SiO, where R represents a variety of organic groups that can be attached to the silicon atoms.
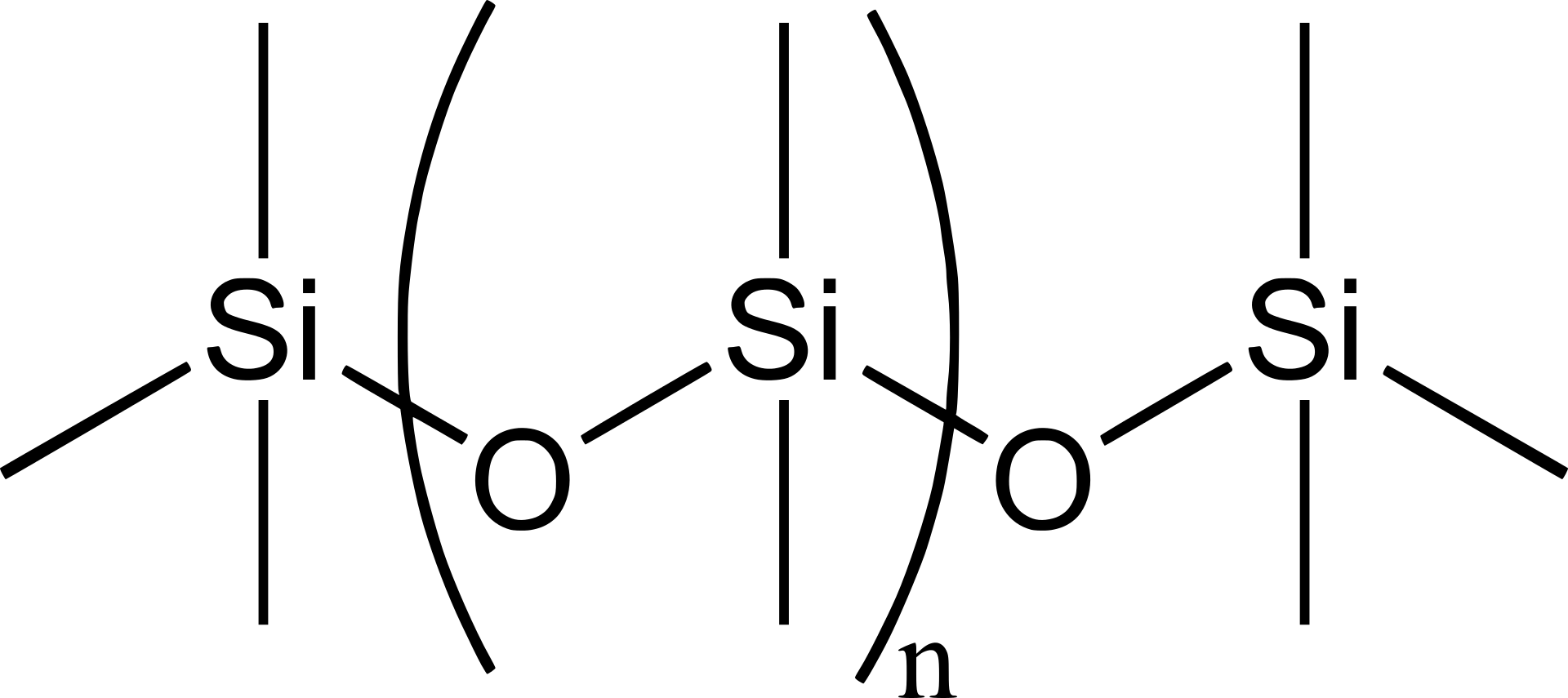
The siloxane chain is the backbone of the silicone polymer, and the properties of the silicone depend on the length of the chain, the type of organic groups attached to the silicon atoms, and the degree of cross-linking between the chains.
One of the unique properties of silicone is its high thermal stability, which is due to the strength of the silicon-oxygen bond. This bond is much stronger than the carbon-carbon bond found in most organic compounds, which makes silicone more resistant to heat and oxidation.
Silicone can also be modified by adding different organic groups to the silicon atoms, which can change its properties. For example, adding methyl groups to the silicon atoms can increase the flexibility of the silicone, while adding phenyl groups can make it more rigid.
Overall, the chemical structure of silicone is what gives it its unique properties, including its high thermal stability, low chemical reactivity, and flexibility. By understanding the chemical structure of silicone, scientists can design new types of silicone with tailored properties for specific applications.
Physical properties of silicone
Silicone has a unique set of physical properties that make it a versatile material for a wide range of applications. Some of the key physical properties of silicone include:
- High temperature resistance: Silicone can withstand high temperatures without degrading or breaking down, making it ideal for use in high-temperature environments.
- Low thermal conductivity: Silicone has a low thermal conductivity, which means it doesn’t transfer heat as quickly as other materials. This makes it useful for insulating applications where heat transfer needs to be minimized.
- High flexibility: Silicone is highly flexible and can be stretched or compressed without breaking. This makes it useful for applications where flexibility is important, such as in seals or gaskets.
- Low toxicity: Silicone is non-toxic and doesn’t leach harmful chemicals, making it safe for use in medical and food-contact applications.
- Water resistance: Silicone is highly water-resistant and doesn’t absorb water, making it useful for applications where exposure to water is a concern.
- UV resistance: Silicone is highly resistant to UV radiation, which makes it useful for outdoor applications where exposure to sunlight is a concern.
- Non-stick properties: Silicone has a non-stick surface that makes it useful for cooking and baking applications, where food can be easily released from silicone molds or baking sheets.
Overall, the physical properties of silicone make it a highly versatile material for a wide range of applications, from construction and engineering to personal care and beauty products. By understanding the physical properties of silicone, engineers and designers can select the right type of silicone for their specific application.
Advantages and disadvantages of silicone
Advantages of Silicone:
- High temperature resistance: Silicone can withstand high temperatures without degrading, making it ideal for use in high-temperature applications.
- Flexibility: Silicone is highly flexible and can be stretched or compressed without breaking, making it useful in applications where flexibility is important.
- Water resistance: Silicone is highly water-resistant and doesn’t absorb water, making it useful in applications where exposure to water is a concern.
- Chemical resistance: Silicone is highly resistant to chemicals, making it useful in applications where exposure to chemicals is a concern.
- Non-toxic: Silicone is non-toxic and doesn’t leach harmful chemicals, making it safe for use in medical and food-contact applications.
- UV resistance: Silicone is highly resistant to UV radiation, making it useful in outdoor applications where exposure to sunlight is a concern.
- Easy to clean: Silicone is easy to clean and can be sterilized, making it useful in applications where hygiene is important.
Disadvantages of Silicone:
- Cost: Silicone can be more expensive than other materials, which can make it less cost-effective for some applications.
- Not as strong as some materials: Silicone is not as strong as some other materials, which can limit its use in high-stress applications.
- Limited color options: Silicone is typically only available in a limited range of colors, which can limit its use in applications where color is important.
- Can be difficult to bond: Silicone can be difficult to bond to other materials, which can limit its use in some applications.
Overall, the advantages of silicone make it a highly versatile material for a wide range of applications, while its disadvantages should be taken into account when selecting the right material for a specific application.
Uses of Silicone
Silicone in construction and engineering
Silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in the construction and engineering industries. Some of the ways that silicone is used in construction and engineering include:
- Sealants and adhesives: Silicone sealants and adhesives are commonly used in construction and engineering to seal gaps and joints, as well as to bond materials together. Silicone sealants and adhesives are highly durable and can withstand exposure to a wide range of chemicals, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures.
- Coatings: Silicone coatings are used in construction and engineering to protect surfaces from damage and corrosion. Silicone coatings can be applied to a wide range of surfaces, including metal, concrete, and masonry, and can provide long-lasting protection against environmental factors like moisture, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures.
- Electrical insulation: Silicone is an excellent electrical insulator, making it useful in a wide range of electrical applications. Silicone can be used to insulate electrical wires and cables, as well as to protect electronic components from moisture and other environmental factors.
- Structural glazing: Silicone structural glazing is a technique used in modern architecture to create a seamless, all-glass facade. Silicone structural glazing involves using silicone sealants and adhesives to bond glass panels to a metal frame, creating a strong, durable, and weather-resistant facade.
- Expansion joints: Silicone expansion joints are used in construction to allow for movement between different parts of a building or structure. Silicone expansion joints are highly flexible and can withstand exposure to a wide range of environmental factors, making them ideal for use in buildings and structures that are subject to movement.
Overall, silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in the construction and engineering industries. By understanding the unique properties of silicone, engineers and designers can select the right type of silicone for their specific application, whether it’s for sealants, coatings, electrical insulation, structural glazing, or expansion joints.
Silicone in the automotive industry
Silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in the automotive industry. Some of the ways that silicone is used in automotive applications include:
- Seals and gaskets: Silicone is commonly used in automotive applications to create seals and gaskets that prevent leaks and protect against environmental factors like heat, cold, and moisture. Silicone seals and gaskets are highly durable and can withstand exposure to a wide range of chemicals and temperatures.
- Hoses and tubing: Silicone hoses and tubing are commonly used in automotive applications to transport fluids like coolant, oil, and fuel. Silicone hoses and tubing are highly flexible and can withstand exposure to high temperatures and pressure, making them ideal for use in high-performance applications.
- Electrical insulation: Silicone is an excellent electrical insulator, making it useful in a wide range of automotive electrical applications. Silicone can be used to insulate electrical wires and cables, as well as to protect electronic components from moisture and other environmental factors.
- Coatings: Silicone coatings are used in automotive applications to protect surfaces from damage and corrosion. Silicone coatings can be applied to a wide range of surfaces, including metal, plastic, and rubber, and can provide long-lasting protection against environmental factors like moisture, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures.
- Adhesives and sealants: Silicone adhesives and sealants are commonly used in automotive applications to bond materials together and to create airtight seals. Silicone adhesives and sealants are highly durable and can withstand exposure to a wide range of chemicals, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures.
Overall, silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in the automotive industry. By understanding the unique properties of silicone, engineers and designers can select the right type of silicone for their specific application, whether it’s for seals and gaskets, hoses and tubing, electrical insulation, coatings, or adhesives and sealants.
Silicone in the medical field
Silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in the medical field. Some of the ways that silicone is used in medical applications include:
- Medical implants: Silicone is commonly used in medical implants, such as breast implants, pacemakers, and artificial joints. Silicone is biocompatible, meaning it doesn’t cause an immune response when implanted in the body, and it can be molded into a wide range of shapes and sizes.
- Medical tubing and catheters: Silicone tubing and catheters are commonly used in medical applications to transport fluids like blood and medication. Silicone tubing and catheters are highly flexible and can be sterilized, making them ideal for use in medical settings.
- Wound care: Silicone is used in wound care products, such as dressings and bandages, to create a non-stick surface that won’t adhere to the wound. Silicone wound care products are highly flexible and can conform to the shape of the wound, providing a comfortable and effective barrier against infection.
- Medical adhesives: Silicone adhesives are used in medical applications to bond materials together, such as in surgical incisions or the attachment of medical devices. Silicone adhesives are biocompatible and can withstand exposure to a wide range of environmental factors, making them ideal for use in medical settings.
- Medical equipment: Silicone is used in a wide range of medical equipment, such as syringes, tubing, and respiratory masks. Silicone is highly flexible and can withstand exposure to high temperatures and pressure, making it ideal for use in medical applications where durability and reliability are important.
Overall, silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in the medical field. By understanding the unique properties of silicone, medical professionals and device manufacturers can select the right type of silicone for their specific application, whether it’s for medical implants, tubing and catheters, wound care, medical adhesives, or medical equipment.
Silicone in household products
Silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in household products. Some of the ways that silicone is used in household products include:
- Kitchenware: Silicone is commonly used in kitchenware, such as baking mats, cooking utensils, and food storage containers. Silicone is non-stick and can withstand exposure to high temperatures, making it ideal for use in cooking and baking applications.
- Personal care products: Silicone is used in a wide range of personal care products, such as makeup brushes, hair brushes, and facial cleansing brushes. Silicone is easy to clean and doesn’t absorb bacteria, making it a hygienic choice for personal care products.
- Electronics accessories: Silicone is used in a wide range of electronics accessories, such as phone cases, keyboard covers, and cable organizers. Silicone is highly durable and can protect electronics from damage and environmental factors like moisture and dust.
- Household cleaning products: Silicone is used in household cleaning products, such as squeegees and scrubbers, to provide a non-abrasive surface that won’t scratch surfaces. Silicone is also easy to clean and can be sterilized, making it ideal for use in cleaning applications.
- Children’s products: Silicone is used in a wide range of children’s products, such as teething toys, pacifiers, and baby bottle nipples. Silicone is non-toxic and doesn’t leach harmful chemicals, making it safe for use in children’s products.
Overall, silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in household products. By understanding the unique properties of silicone, designers and manufacturers can create products that are durable, hygienic, and safe for use in a wide range of applications.
Silicone in personal care and beauty products
Silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in personal care and beauty products. Some of the ways that silicone is used in personal care and beauty products include:
- Hair care products: Silicone is commonly used in hair care products, such as shampoos, conditioners, and styling products. Silicone helps to smooth and protect the hair, reducing frizz and improving shine. It can also help to protect hair from heat damage caused by styling tools like flat irons and curling wands.
- Skin care products: Silicone is used in a wide range of skin care products, such as moisturizers, serums, and primers. Silicone helps to create a smooth, silky texture that can help to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. It can also help to protect the skin from environmental factors like pollution and UV radiation.
- Makeup products: Silicone is used in a wide range of makeup products, such as foundations, primers, and eye shadows. Silicone helps to create a smooth, even texture that can help to improve the appearance of the skin. It can also help to improve the longevity of makeup products by creating a barrier that helps to prevent smudging and fading.
- Sunscreen products: Silicone is used in some sunscreen products to create a smooth, even texture that can help to improve the application and effectiveness of the sunscreen. Silicone can also help to protect the skin from environmental factors like pollution and UV radiation.
- Fragrance products: Silicone is used in some fragrance products, such as perfumes and colognes, to help extend the life of the fragrance. Silicone can help to slow down the evaporation of the fragrance, helping it to last longer on the skin.
Overall, silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in personal care and beauty products. By understanding the unique properties of silicone, designers and manufacturers can create products that are effective, long-lasting, and provide a smooth, silky texture that can help to improve the appearance of the skin and hair.
How Silicone Is Made
Raw materials used in silicone production
Silicone is a synthetic material that is made from a combination of silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The raw materials used in silicone production include:
- Silica: Silica is a compound found in sand and rocks. It is the primary source of silicon used in silicone production.
- Carbon: Carbon is used in the production of silicon metal, which is a key ingredient in silicone production.
- Methyl chloride: Methyl chloride or other organic compounds are used to react with silicon metal to produce silicone monomers.
- Hydrogen: Hydrogen is used in the production of silicone monomers and polymers.
- Catalysts: Catalysts, such as platinum, are used to speed up the reaction between the silicon metal and organic compounds to produce silicone monomers.
Overall, the raw materials used in silicone production are relatively simple and readily available, with silica being the primary source of silicon used in the process.
Steps in the silicone manufacturing process
The process of making silicone involves several steps, including:
- Production of silicon metal: Silica is heated with carbon in a furnace to produce silicon metal.
- Production of silicone monomers: The silicon metal is then reacted with methyl chloride or other organic compounds to produce silicone monomers.
- Polymerization: The silicone monomers are polymerized, or joined together, to form silicone polymers. This is typically done using a catalyst, such as platinum.
- Modification: The silicone polymers can be modified to give them specific properties, such as increased flexibility or water resistance.
- Processing: The final step in making silicone is processing the material into its final form. This can involve extrusion, molding, or other techniques to create products such as sealants, adhesives, coatings, and other materials.
Overall, the process of making silicone involves several steps, from the production of silicon metal to the polymerization of silicone monomers and the modification of the resulting polymers. By understanding the steps involved in the silicone manufacturing process, manufacturers can create products with specific properties and characteristics to meet the needs of a wide range of applications.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Silicone is a synthetic material that has a wide range of applications in various industries, including personal care, medical, and household products. One of the most common questions people have about silicone is whether it is safe to use. The answer is generally yes, as silicone is considered to be a safe material for use in a wide range of applications.
Here are some reasons why silicone is considered to be a safe material:
- Biocompatibility: Silicone is biocompatible, meaning it does not cause an immune response when implanted in the body. This makes it a safe choice for medical implants, such as breast implants and pacemakers.
- Non-toxic: Silicone is non-toxic and does not leach harmful chemicals, making it safe for use in food contact applications, such as kitchenware and baby products.
- Heat resistance: Silicone can withstand high temperatures without melting or releasing harmful fumes, making it safe for use in cooking and baking applications.
- Easy to clean: Silicone is easy to clean and does not absorb bacteria, making it a hygienic choice for personal care products, such as makeup brushes and facial cleansing brushes.
- Durable: Silicone is highly durable and can withstand exposure to a wide range of environmental factors, making it a safe choice for use in a wide range of applications.
While silicone is generally considered to be a safe material, it is important to note that not all silicone products are created equal. Some products may contain additives or impurities that could be harmful, so it is important to choose high-quality silicone products from reputable manufacturers.
Overall, silicone is a safe and versatile material that has a wide range of applications in various industries. By understanding the unique properties of silicone and choosing high-quality products, consumers can use silicone products safely and confidently.
Environmental impact of silicone production and disposal
Silicone is a synthetic material that has a wide range of applications in various industries, including personal care, medical, and household products. While silicone is considered to be a safe and versatile material, its production and disposal can have environmental impacts.
Here are some of the environmental impacts associated with silicone production and disposal:
- Energy consumption: The production of silicone requires a significant amount of energy, primarily in the form of electricity. This can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental impacts associated with energy production.
- Waste generation: The production of silicone can generate waste materials, such as silica dust and other byproducts. These waste materials can be harmful to the environment if not properly managed.
- Land use: The production of silicone may require the use of land for mining of raw materials, such as sand. This can have environmental impacts, such as habitat destruction and soil erosion.
- Disposal: While silicone is generally considered to be a safe and durable material, its disposal can have environmental impacts. Silicone products may take a long time to decompose in landfills, and burning them can release harmful chemicals into the air.
To minimize the environmental impacts of silicone production and disposal, manufacturers and consumers can take several steps, such as:
- Using recycled materials: Some manufacturers are using recycled materials in the production of silicone, which can reduce the environmental impacts associated with mining and processing of raw materials.
- Proper waste management: Manufacturers can implement proper waste management practices to minimize the environmental impacts of waste generated during silicone production.
- Recycling: Some silicone products can be recycled, which can reduce the amount of waste generated and the need for new raw materials.
- Proper disposal: Consumers can dispose of silicone products properly by recycling them if possible or disposing of them in a landfill.
Overall, while silicone has many benefits and applications, its production and disposal can have environmental impacts. By taking steps to reduce waste, use recycled materials, and properly dispose of silicone products, we can minimize the environmental impacts of this versatile material.
Conclusion
Recap of key points about silicone
Silicone is a synthetic material that has a wide range of applications in various industries, including personal care, medical, and household products. Here are some key points to remember about silicone:
- Silicone is a synthetic material made from a combination of silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen.
- Silicone is a versatile material that can be modified to give it specific properties, such as increased flexibility or water resistance.
- Silicone is considered to be a safe material for use in a wide range of applications, including medical implants, food contact applications, and personal care products.
- Silicone is biocompatible, non-toxic, heat-resistant, easy to clean, and highly durable.
- The production and disposal of silicone can have environmental impacts, such as energy consumption, waste generation, and land use.
To use silicone safely and responsibly, it is important to choose high-quality products from reputable manufacturers, properly dispose of silicone products, and take steps to minimize waste and reduce environmental impacts. By understanding the unique properties and applications of silicone, we can make informed choices about the products we use and their impact on our health and the environment.
Future outlook for silicone
Silicone is a highly versatile material that has a wide range of applications in various industries. As technology and innovation continue to advance, the future outlook for silicone is promising, with new applications and uses being developed all the time.
Here are some potential future developments and trends for silicone:
- Smart materials: Silicone can be modified to create smart materials that can respond to changes in their environment, such as temperature or moisture. These materials could have a wide range of applications in industries such as healthcare, where they could be used in sensors or drug delivery systems.
- Sustainable production: As environmental concerns continue to grow, there is an increasing focus on developing sustainable production methods for silicone. This could involve using renewable energy sources, reducing waste and emissions, and using recycled materials.
- New applications: With its unique properties, silicone has the potential to be used in many new applications and industries. For example, it could be used in 3D printing, where its flexibility and durability could make it an ideal material for creating complex shapes and structures.
- Nanotechnology: Silicone nanoparticles are being developed for use in a wide range of applications, such as drug delivery and wound healing. These nanoparticles could have unique properties that make them more effective than traditional materials.
Overall, the future outlook for silicone is promising, with new developments and applications being discovered all the time. As technology and innovation continue to advance, silicone is likely to play an increasingly important role in various industries, from healthcare to electronics to construction.